- sales/support
Google Chat:---
- sales
+86-0755-88291180
- sales01
sales@spotpear.com
- sales02
dragon_manager@163.com
- support
tech-support@spotpear.com
- CEO-Complaints
zhoujie@spotpear.com
- sales/support
WhatsApp:13246739196
- HOME
- >
- ARTICLES
- >
- Common Moudle
- >
- ESP
ESP32-S3-RLCD-4.2-EN User Guide
ESP32-S3-RLCD-4.2
This product is a fully reflective screen AIoT development board based on the ESP32-S3, supporting dual-mode communication with Wi-Fi and BLE. It features a 4.2inch fully reflective display (RLCD), low power consumption, display performance close to that of an e-Paper screen, and faster refresh response. It includes onboard audio codec circuitr, dual microphones, speaker, SHTC3 high-precision temperature and humidity sensor, TF card slot, RTC interface, and battery charge and discharge management circuit, etc. It also reserves USB, UART, I2C, and multiple GPIO interfaces for convenient expansion. It supports AI voice, temperature and humidity monitoring, and IoT control, and is suitable for DIY desktop smart ornaments, electronic calendars, AI agents, etc., and can also be used for product prototype development.
Features
- Equipped with a high-performance Xtensa® 32-bit LX7 dual-core processor clocked at up to 240MHz
- Supports 2.4GHz Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5 (LE), with built-in antenna
- Built-in 512KB SRAM, 384KB ROM, stacked with 16MB Flash and 8MB PSRAM integrated
- Equipped with a 4.2inch fully reflective screen with a resolution of 300 × 400, featuring characteristics of reflection imaging and no backlight required
- Equipped with a dual-microphone array for audio algorithms such as noise reduction and echo cancellation, suitable for accurate speech recognition and near-field/far-field wake-up applications
- Onboard PCF85063 RTC real-time clock and SHTC3 temperature and humidity sensor for precise RTC time management and temperature and humidity monitoring
- Onboard 18650 lithium battery holder and RTC backup battery holder (requires a rechargeable RTC battery), supporting dual modes of main power supply and independent RTC power backup
- Built-in TF card slot, supports external storage of images or files
- Onboard KEY and BOOT two side buttons with customizable functions, allowing for custom function development
- Reserved 2 × 8 female header interface (2.54mm pitch) for convenient external expansion
Onboard Resources
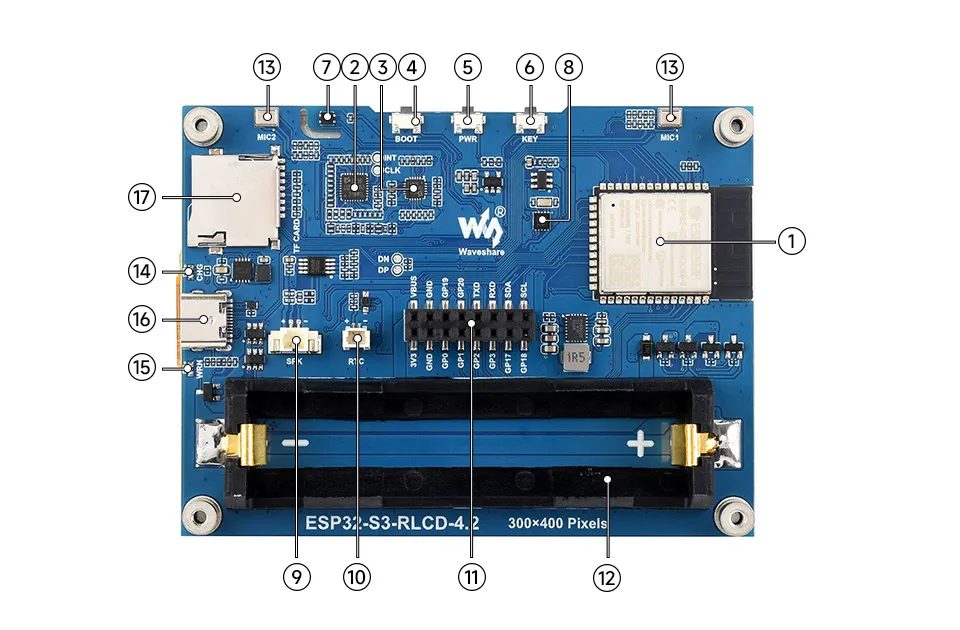
- ESP32-S3-WROOM-1-N16R8 Wi-Fi and Bluetooth SoC, up to 240MHz operating frequency, stacked with 16MB Flash and 8MB PSRAM
- ES7210 ADC chip implements echo cancellation circuit
- ES8311 Low power audio codec IC
- BOOT Button Press and hold the BOOT button to power on again to enter download mode
- PWR Button Long press to power off, single click to power on
- KEY Button Customizable function button
- SHTC3 Temperature and Humidity Sensor Provides ambient temperature and humidity measurement, enabling environmental monitoring function
- PCF85063 RTC clock chip, supporting time-keeping functionality
- MX1.25 2PIN Speaker Interface Audio signal output, for connecting external speaker
- RTC Independent Power Interface Supports only PH1.0 rechargeable RTC battery
- 2 × 8PIN 2.54mm Pitch Female Header
- 18650 Battery Holder
- Dual Microphone Array Design Dual microphone array with ES7210 for echo cancellation
- CHG Charging Indicator Light The light turns off when the battery is fully charged
- WRN Warning Indicator Light The light stays on if the battery is reverse-connected
- Type-C Interface Used for program flashing and log printing
- TF Card Slot Supports FAT32-formatted TF card for data expansion
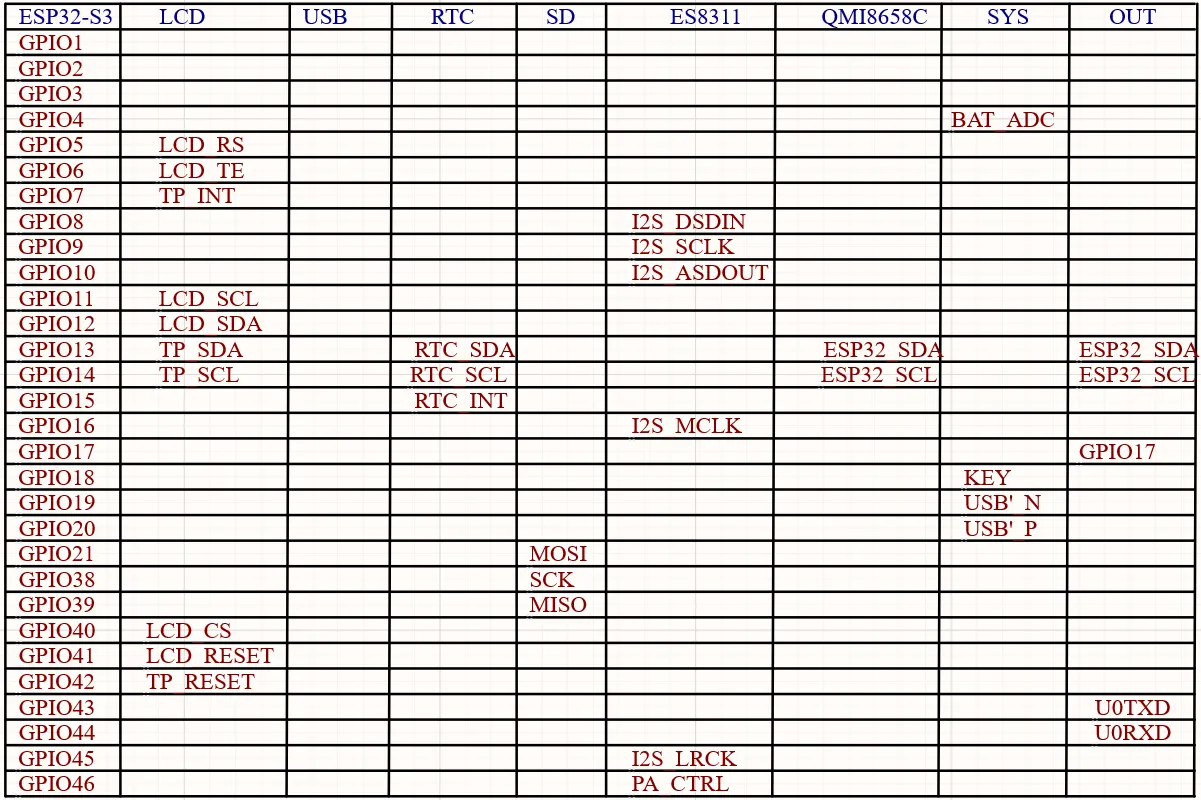
Interfaces
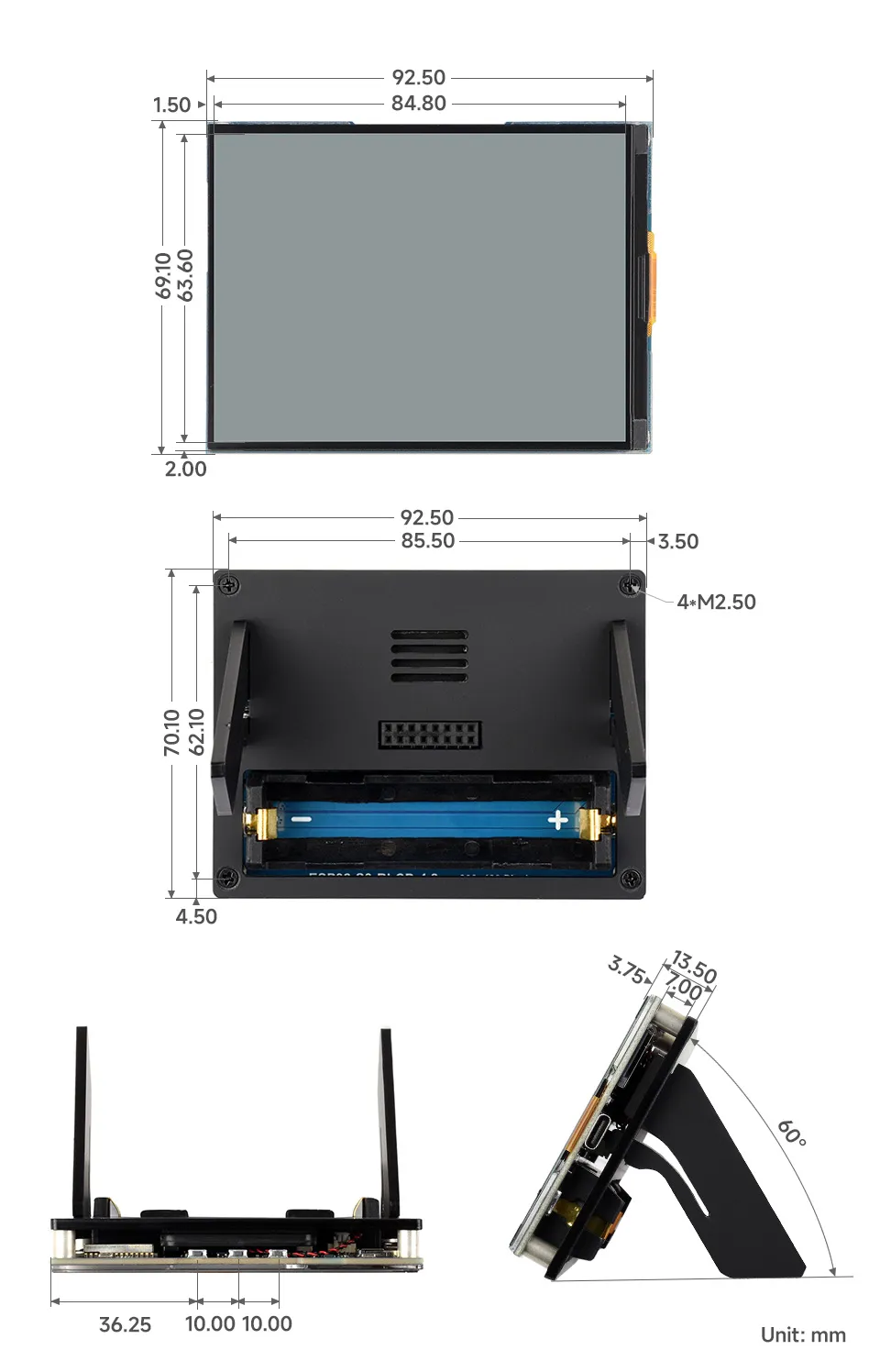
Dimensions
Working with Arduino
This chapter includes the following sections, please read as needed:
- Arduino Getting Started
- Setting Up Development Environment
- Demo
Setting Up Development Environment
1. Installing and Configuring Arduino IDE
Please refer to the tutorial Installing and Configuring Arduino IDE Tutorial to download and install the Arduino IDE and add ESP32 support.
2. Installing Libraries
- When installing Arduino libraries, there are typically two methods: Online Installation and Offline Installation. If the library installation requires offline installation, you must use the provided library file.
- For most libraries, users can easily search and install them through the online Library Manager in the Arduino software. However, some open-source libraries or custom libraries are not synchronized to the Arduino Library Manager, so they cannot be acquired through online searches. In this case, users can only manually install these libraries offline.
- The sample program package for the ESP32-S3-RLCD-4.2 development board can be downloaded from here. The
Arduino\librariesdirectory within the package already includes all the library files required for this tutorial.
| Library/File Name | Description | Version | Installation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| LVGL | Graphical library | v8.3.11/v9.3.0 | |
| SensorLib | Sensor library | v0.3.1 | "Install Online" or "Install Offline" |
:::Warning Version Compatibility Description
There are strong dependencies between versions of LVGL and its driver libraries. For example, a driver written for LVGL v8 may not be compatible with LVGL v9. To ensure stable reproduction of the examples, it is recommended to use the specific versions listed in the table above. Mixing different library versions may cause compilation failures or runtime exceptions. :::
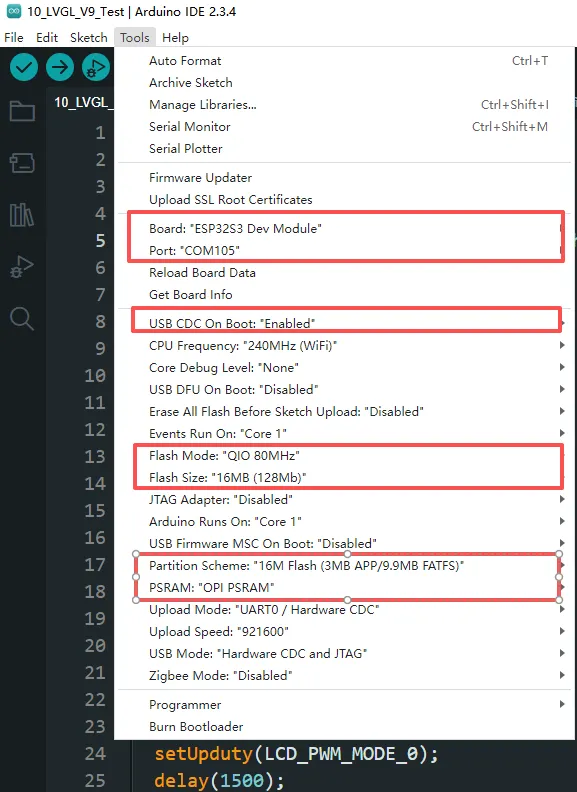
3. Arduino Project Parameter Settings
Demo
The Arduino demos are located in the Arduino/examples directory of the demo package.
| Demo | Basic Program Description | Dependency Library |
|---|---|---|
| 01_WIFI_AP | Set to AP mode to obtain the IP address of the access device | - |
| 02_WIFI_STA | Set to STA mode to connect to WiFi and obtain an IP address | - |
| 03_ADC_Test | Get the voltage value of the lithium battery | - |
| 04_I2C_PCF85063 | Print real-time time of RTC chip | SensorLib |
| 05_I2C_SHTC3 | Print temperature and humidity sensor data | - |
| 06_SD_Card | Load and display the information of the TF card | - |
| 07_Audio_Test | Play the sound recorded by the microphone through the speaker | LVGL V8.3.11 |
| 08_LVGL_V8_Test | LVGLV8 demo | LVGL V8.3.11 |
| 09_LVGL_V9_Test | LVGLV9 demo | LVGL V9.3.0 |
01_WIFI_AP
Demo Description
- This demo can set the development board as a hotspot, allowing phones or other devices in STA mode to connect to the development board.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
*In the file 01_WIFI_AP.ino, find ssid and password, then a phone or other device in STA mode can connect to the development board using these ssid and password.
const char *ssid = "ESP32_AP";
const char *password = "12345678";
Expected Result
After the program is compiled and downloaded, you can view the printed ADC values and voltage output by opening the Serial Monitor, as shown in the following image:
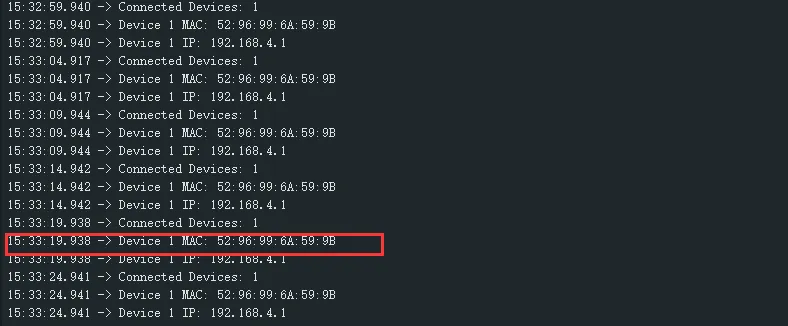
02_WIFI_STA
Demo Description
- This example can configure the development board as a STA device to connect to a router, thereby enabling access to the system network.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
In the file
02_WIFI_STA.ino, findssidandpassword, then modify them to the SSID and Password of an available router in your current environment.const char *ssid = "you_ssid";
const char *password = "you_password";
Expected Result
After flashing the program, open the serial terminal, if the device is successfully connected to the hotspot, the IP address obtained will be output, as shown in the figure:
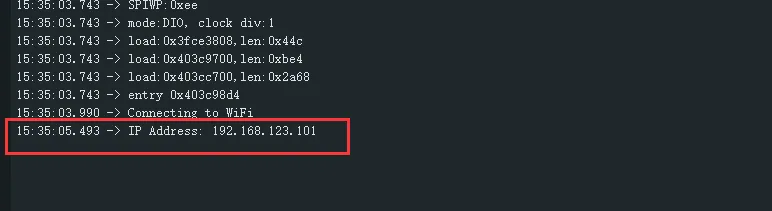
03_ADC_Test
Demo Description
- The analog voltage connected through the GPIO is converted to digital by the ADC, and then the actual lithium battery voltage is calculated and printed to the terminal.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
Adc_PortInit(void): Initializes ADC1, including creating an ADC one-time trigger unit and configuring channel 3 for ADC1float Adc_GetBatteryVoltage(int *data): Reads the value from ADC1 channel 3 and returns the actual voltage value.uint8_t Adc_GetBatteryLevel(void): Returns the battery percentage.void Adc_LoopTask(void *arg): Creates an ADC task that reads the ADC value and prints it to the serial port every second.
Expected Result
After the program is compiled and downloaded, you can view the printed ADC values and voltage output by opening the Serial Monitor, as shown in the following image:
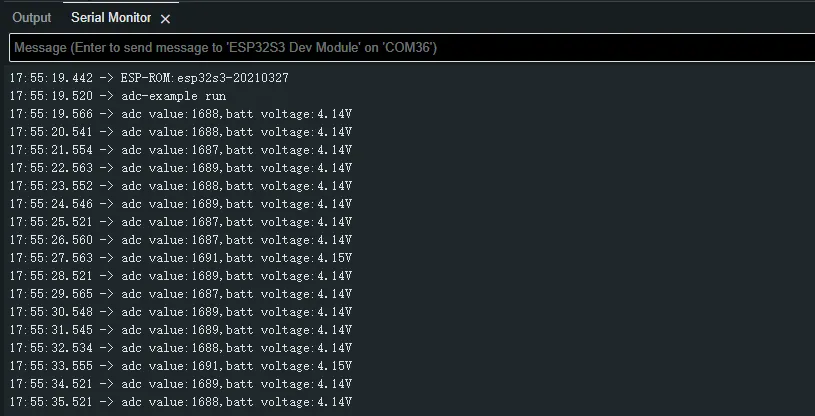
04_I2C_PCF85063
Demo Description
- Through the I2C protocol, initialize the PCF85063 chip, set the time, and then periodically read the time and print it to the terminal
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
I2cMasterBus I2cbus(14,13,0); // Initialize I2C bus
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
Serial.printf("rtc-example run \n");
Rtc_Setup(&I2cbus, 0x51); // Initialize RTC, set RTC slave address to 0x51
Rtc_SetTime(2025, 9, 9, 20, 15, 30); // Set RTC time
}
void loop() {
rtcTimeStruct_t rtcData;
Rtc_GetTime(&rtcData); // Get the real-time clock (RTC) time
Serial.printf("%d/%d/%d %02d:%02d:%02d \n",
rtcData.year, rtcData.month, rtcData.day, rtcData.hour, rtcData.minute,
rtcData.second);
delay(1000);
}
Expected Result
After the program is compiled and downloaded, open the serial port monitoring to see the RTC time of the printout, as shown in the following figure:
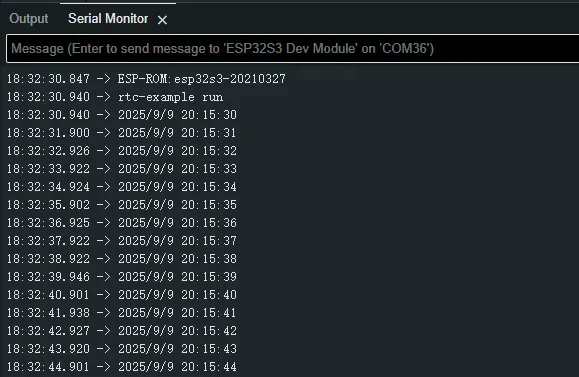
05_I2C_SHTC3
Demo Description
- Initialize the SHTC3 chip through the I2C protocol, and then print the temperature and humidity information read every 1 second to the terminal
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
I2cMasterBus I2cbus(14,13,0);
Shtc3Port *shtc3port = NULL;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
Serial.printf("shtc3-example run \n");
shtc3port = new Shtc3Port(I2cbus); // Initialize SHTC3
}
void loop() {
float rh,temp;
shtc3port->Shtc3_ReadTempHumi(&temp,&rh); // Get temperature and humidity data
Serial.printf("RH:%.2f%%,Temp:%.2f° \n",rh,temp);
delay(1000);
}
Expected Result
Open the serial port monitor, you can see the printed temperature and humidity data, as shown in the figure below:
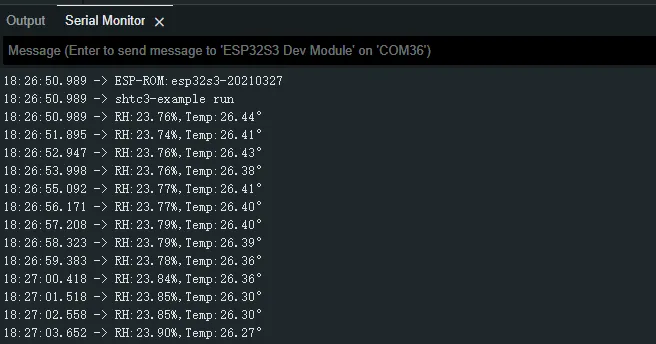
06_SD_Card
Demo Description
- Drive the TF card through SDMMC, and print the TF card information to the terminal after successfully mounting.
Hardware Connection
- Install a FatFs-formatted into the board before powering on
Code Analysis
#define sdcard_write_Test
CustomSDPort *sdcardPort = NULL;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(2000);
sdcardPort = new CustomSDPort("/sdcard"); // Initialize SDMMC driver
}
uint32_t value = 1;
char sdcard_read[45] = {""};
char sdcard_write[45] = {""};
void loop()
{
#ifdef sdcard_write_Test // Test the TF card read/write functionality
snprintf(sdcard_write,45,"sdcard_writeTest : %ld \n",value);
sdcardPort->SDPort_WriteFile("/sdcard/writeTest.txt",sdcard_write,strlen(sdcard_write));
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(500));
sdcardPort->SDPort_ReadFile("/sdcard/writeTest.txt",(uint8_t *)sdcard_read,NULL);
Serial.printf("read data:%s\n",sdcard_read);
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(500));
value++;
#endif
}
Expected Result
Click on the serial port monitoring device, you can see the output information of the TF card, as shown in the figure below:
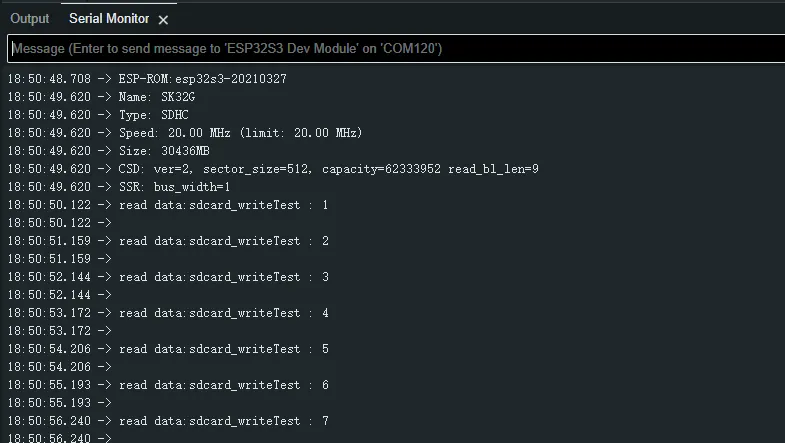
07_Audio_Test
Demo Description
- Demonstrates how to get data from the microphone and then play it through the speaker
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
CodecPort_SetInfo("es8311 & es7210",1,16000,2,16): Sets the sampling rate, number of channels, and bit depth of the Codec chip.CodecPort_SetSpeakerVol(100): Set the playback gain to 100.CodecPort_SetMicGain(35): Set the microphone gain to 35.Codec_LoopTask(void *arg): Codec task, which implements recording, playback, and other functions.
Expected Result
After the program is flashed, as shown in the figure:
 TIP
TIP- Double-click the BOOT button to enter recording mode, speak into the MIC, and it will automatically end after 3 seconds
- Click the BOOT button to play the sound you just recorded
- Double-click the KEY button to play a piece of music
- Click the KEY button to interrupt music playback
08_LVGL_V8_Test
Demo Description
- Demonstrates how to display images using LVGL V8, helping users get started quickly with LVGL V8.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_1 = lv_img_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_1, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_img_set_src(ui->screen_img_1, &_ein_alpha_400x300);
lv_img_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_1, 50,50);
lv_img_set_angle(ui->screen_img_1, 0);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_1, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_1, 400, 300);
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_2 = lv_img_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_img_set_src(ui->screen_img_2, &_2_alpha_400x300);
lv_img_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_2, 50,50);
lv_img_set_angle(ui->screen_img_2, 0);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_2, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_2, 400, 300);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_HIDDEN);
Expected Result
After the program is flashed, it is displayed alternately at intervals of 1.5 seconds, as shown in the figure:

09_LVGL_V9_Test
Demo Description
- Demonstrates how to display images using LVGL V9, helping users get started quickly with LVGL V9.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_1 = lv_image_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_1, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_1, 400, 300);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_1, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_image_set_src(ui->screen_img_1, &_ein_RGB565A8_400x300);
lv_image_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_1, 50,50);
lv_image_set_rotation(ui->screen_img_1, 0);
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_2 = lv_image_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_2, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_2, 400, 300);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_HIDDEN);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_image_set_src(ui->screen_img_2, &_2_RGB565A8_400x300);
lv_image_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_2, 50,50);
lv_image_set_rotation(ui->screen_img_2, 0);
Expected Result
After the program is flashed, it is displayed alternately at intervals of 1.5 seconds, as shown in the figure:

ESP-IDF
Demo
The ESP-IDF demo is located in the
ESP-IDFdirectory of the example.Demo Basic Program Description Dependency Library 01_WIFI_AP Set to AP mode to obtain the IP address of the access device - 02_WIFI_STA Set to STA mode to connect to WiFi and obtain an IP address - 03_ADC_Test Get the voltage value of the lithium battery - 04_I2C_PCF85063 Print real-time time of RTC chip SensorLib 05_I2C_SHTC3 Print temperature and humidity sensor data - 06_SD_Card Load and display the information of the TF card - 07_Audio_Test Play the sound recorded by the microphone through the speaker LVGL V8.3.11 08_LVGL_V8_Test LVGLV8 demo LVGL V8.3.11 09_LVGL_V9_Test LVGLV9 demo LVGL V9.3.0 10_FactoryProgram Comprehensive demo LVGL V8.3.11 01_WIFI_AP
Demo Description
- This demo can set the development board as a hotspot, allowing phones or other devices in STA mode to connect to the development board.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
In the file
softap_example_main.c, findSSIDandPASSWORD, and then your phone or other device in STA mode can use the SSID and PASSWORD to connect to the development board.#define EXAMPLE_ESP_WIFI_SSID "waveshare_esp32"
#define EXAMPLE_ESP_WIFI_PASSWORD "wav123456"
Expected Result
After flashing the program, open the serial terminal, if the device is successfully connected to the hotspot, the MAC address and IP address of the device will be output, as shown in the figure:
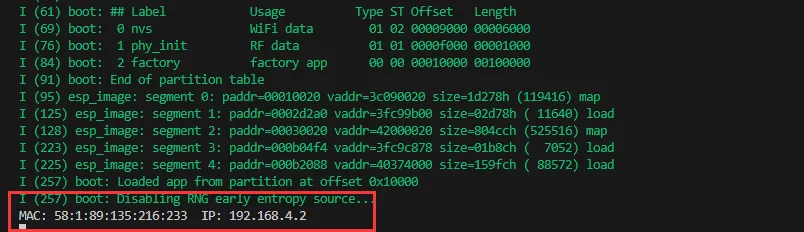
02_WIFI_STA
Demo Description
- This example can configure the development board as a STA device to connect to a router, thereby enabling access to the system network.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
In the file
esp_wifi_bsp.c, findssidandpassword, then modify them to the SSID and Password of an available router in your current environment.wifi_config_t wifi_config = {
.sta = {
.ssid = "PDCN",
.password = "1234567890",
},
};
Expected Result
After flashing the program, open the serial terminal, if the device is successfully connected to the hotspot, the IP address obtained will be output, as shown in the figure:
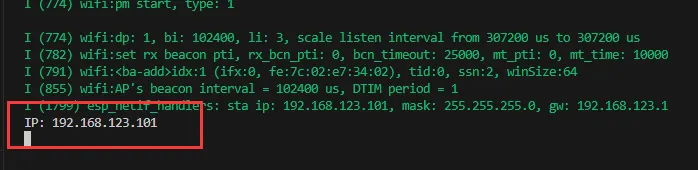
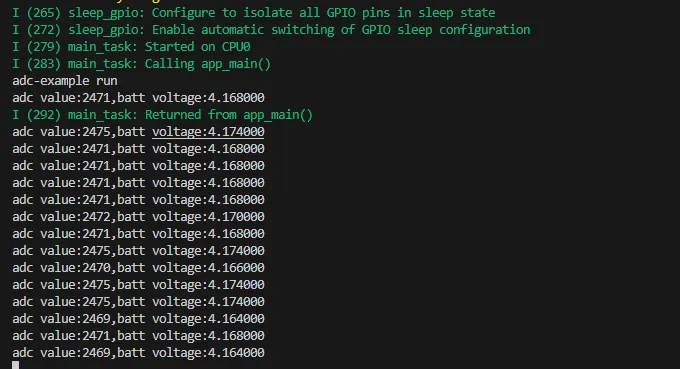
03_ADC_Test
Demo Description
- The analog voltage connected through the GPIO is converted to digital by the ADC, and then the actual lithium battery voltage is calculated and printed to the terminal.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
Adc_PortInit(void): Initializes ADC1, including creating an ADC one-time trigger unit and configuring channel 3 for ADC1float Adc_GetBatteryVoltage(int *data): Reads the value from ADC1 channel 3 and returns the actual voltage value.uint8_t Adc_GetBatteryLevel(void): Returns the battery percentage.void Adc_LoopTask(void *arg): Creates an ADC task that reads the ADC value and prints it to the serial port every second.
Expected Result
After the program is compiled and downloaded, you can view the printed ADC values and voltage output by opening the Serial Monitor, as shown in the following image:
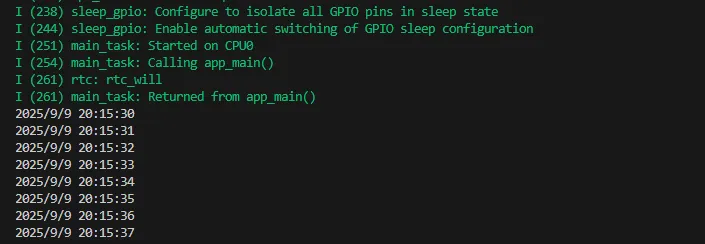
04_I2C_PCF85063
Demo Description
- Through the I2C protocol, initialize the PCF85063 chip, set the time, and then periodically read the time and print it to the terminal
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
void Rtc_LoopTask(void *arg): Create an RTC task to implement the RTC function, read the clock of the RTC chip every 1 second, and then output it to the terminal.
Expected Result
After the program is compiled and downloaded, open the serial port monitoring to see the RTC time of the printout, as shown in the following figure:
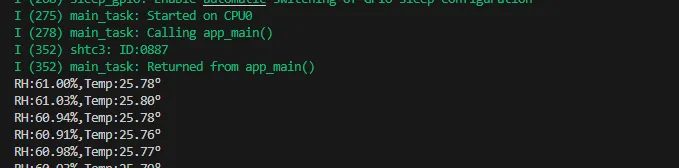
05_I2C_STHC3
Demo Description
- Initialize the SHTC3 chip through the I2C protocol, and then print the temperature and humidity information read every 1 second to the terminal
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
void Shtc3_LoopTask(void *arg): Create a SHTC3 sensor task that obtains temperature and humidity at intervals of 1 second.
Expected Result
Open the serial port monitor, you can see the printed temperature and humidity data, as shown in the figure below:
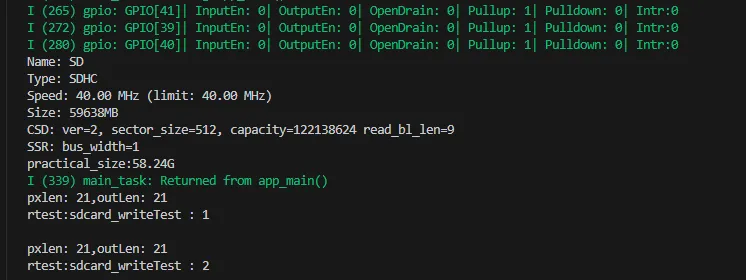
06_SD_Card
Demo Description
- Drive the TF card through SDMMC, and print the TF card information to the terminal after successfully mounting.
Hardware Connection
- Install a FatFs-formatted into the board before powering on
Code Analysis
Fatfs_LoopTask(void *arg): A task to test TF card read and write functionality. You need to uncomment the#define sdcard_write_Testmacro definition.
Expected Result
Click on the serial port monitoring device, you can see the output information of the TF card, as shown in the figure below:
07_Audio_Test
Demo Description
- Demonstrates how to get data from the microphone and then play it through the speaker
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
CodecPort_SetInfo("es8311 & es7210",1,16000,2,16): Sets the sampling rate, number of channels, and bit depth of the Codec chip.CodecPort_SetSpeakerVol(100): Set the playback gain to 100.CodecPort_SetMicGain(35): Set the microphone gain to 35.Codec_LoopTask(void *arg): Codec task, which implements recording, playback, and other functions.
Expected Result
After the program is flashed, as shown in the figure:
 TIP
TIP- Double-click the BOOT button to enter recording mode, speak into the MIC, and it will automatically end after 3 seconds
- Click the BOOT button to play the sound you just recorded
- Double-click the KEY button to play a piece of music
- Click the KEY button to interrupt music playback
08_LVGL_V8_Test
Demo Description
- Demonstrates how to display images using LVGL V8, helping users get started quickly with LVGL V8.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_1 = lv_img_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_1, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_img_set_src(ui->screen_img_1, &_ein_alpha_400x300);
lv_img_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_1, 50,50);
lv_img_set_angle(ui->screen_img_1, 0);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_1, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_1, 400, 300);
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_2 = lv_img_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_img_set_src(ui->screen_img_2, &_2_alpha_400x300);
lv_img_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_2, 50,50);
lv_img_set_angle(ui->screen_img_2, 0);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_2, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_2, 400, 300);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_HIDDEN);Expected Result
After the program is flashed, it is displayed alternately at intervals of 1.5 seconds, as shown in the figure:

09_LVGL_V9_Test
Demo Description
- Demonstrates how to display images using LVGL V9, helping users get started quickly with LVGL V9.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_1 = lv_image_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_1, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_1, 400, 300);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_1, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_image_set_src(ui->screen_img_1, &_ein_RGB565A8_400x300);
lv_image_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_1, 50,50);
lv_image_set_rotation(ui->screen_img_1, 0);
/*Create an IMG1 control*/
ui->screen_img_2 = lv_image_create(ui->screen);
lv_obj_set_pos(ui->screen_img_2, 0, 0);
lv_obj_set_size(ui->screen_img_2, 400, 300);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_HIDDEN);
lv_obj_add_flag(ui->screen_img_2, LV_OBJ_FLAG_CLICKABLE);
lv_image_set_src(ui->screen_img_2, &_2_RGB565A8_400x300);
lv_image_set_pivot(ui->screen_img_2, 50,50);
lv_image_set_rotation(ui->screen_img_2, 0);Expected Result
After the program is flashed, it is displayed alternately at intervals of 1.5 seconds, as shown in the figure:

10_FactoryProgram
Demo Description
- The driver board integrates all hardware components and provides comprehensive examples, enabling users to quickly understand the product.
Hardware Connection
- Connect the board to the computer using a USB cable
Code Analysis
sdcardPort = new CustomSDPort("/sdcard"); // Initialize sdcard
Adc_PortInit(); // Initialize Adc
Custom_ButtonInit(); // Initialize buttons
Rtc_Setup(&I2cbus,0x51); // Initialize RTC
Rtc_SetTime(2026,1,5,14,30,30); // Set RTC time
shtc3port = new Shtc3Port(I2cbus); // Initialize SHTC3
espwifi_init(); // Initialize WiFi STA mode
CodecGroups = xEventGroupCreate();
codecport = new CodecPort(I2cbus,"S3_RLCD_4_2"); // Initialize Codec
codecport->CodecPort_SetInfo("es8311 & es7210",1,16000,2,16);
codecport->CodecPort_SetSpeakerVol(100); // Set the speaker gain
codecport->CodecPort_SetMicGain(35); // Set the microphone gainExpected Result
After the program is flashed, the main interface is displayed, as shown in the figure:

Resources
1. Hardware Resources
Development Board Design File
- Schematic: ESP32-S3-RLCD-4.2-Schematic.pdf
- Structure and dimensions: ESP32-S3-RLCD-4.2-3dFile.rar
2. Technical Manuals
Official ESP32-S3 Chip Manuals
- Datasheets:
- Technical Manuals:
Onboard Component Datasheets
3. Demo
- ESP32-S3-RLCD-4.2 Demo (Github)
Support
Monday-Friday (9:30-6:30) Saturday (9:30-5:30)
Email: services01@spotpear.com




